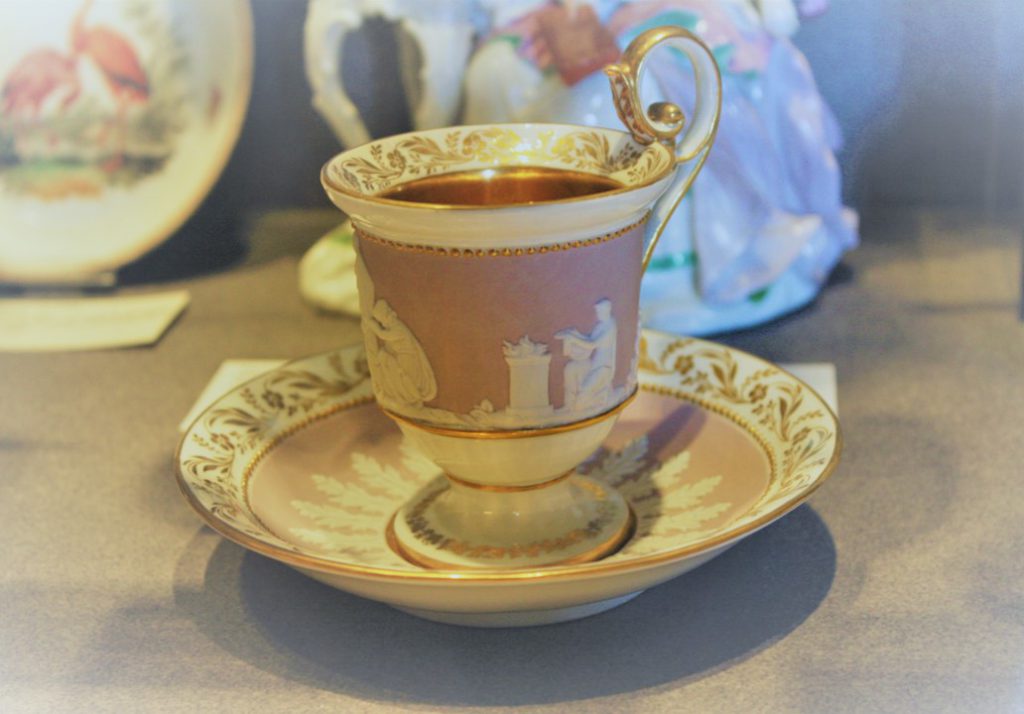
Lord Stanhope (left) and Kaspar Hauser (right)
On 14 December 1833 in Ansbach, a small town in Bavaria, a young man staggers home with a deep wound in his left breast. He states that he was lured to the Court Garden where a stranger stabbed him while giving him a small bag. The young man is known as Kasper Hauser, a local celebrity of his time, and also a mysterious youth of unknown origin.
A policeman searches the Court Garden. He finds a purse containing a note in mirror writing indicating in riddled form the attacker’s identity. He finds neither the weapon involved nor any other helpful evidence. Kasper Hauser dies of his wound three days later.
The death of Kasper Hauser in 1833 is a one of the most famed-famous unsolved cases of criminology. Until today, we don’t know for sure whether the young man was murdered or died by inflicting himself a wound with a knife that penetrated much deeper than he had intended. Until today, we don’t even know who Kasper Hauser was: an imposter, a hereditary prince, an innocent boy?
The story of Kaspar Hauser, a ‘feral child’, who claimed to have lived in isolation and captivity, has all ingredients of a novel of Mrs. Radcliffe: political intrigue, espionage, and conspiracy theories. But what has the English aristocrat, Philip Henry Lord Stanhope, 4. Earl Stanhope (1781-1855), to do with the young man, his secret and his death? Continue reading →