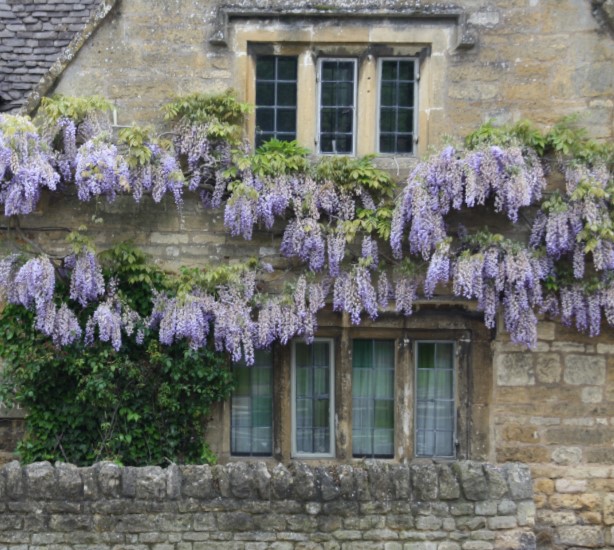
The purple-blue blossoms of the wisteria delight the eye, and their sweet fragrance enchants the soul. Today, this beautiful plant adorns gardens, cottages and manor houses across Britain. The popular Regency-era series Bridgerton shows Bridgerton House with wisteria in full bloom climbing up the facade. But is this historically accurate? Did wisterias bloom in gardens during the Regency period? And would Jane Austen have enjoyed the blossoms, too? Let’s find out.
Continue reading