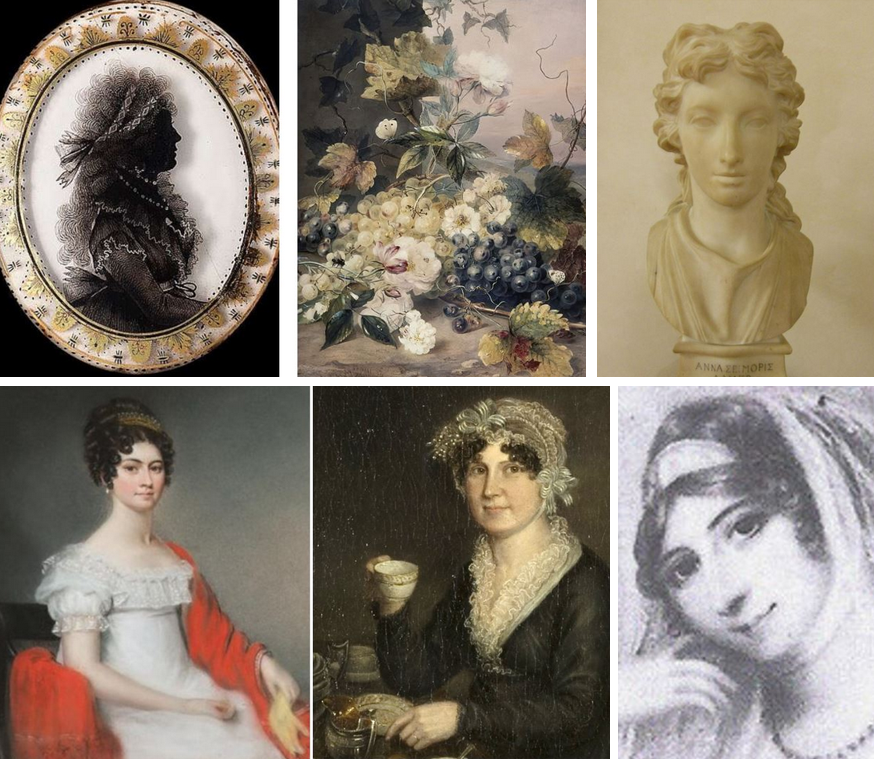
Art had long been the domain of men. However, from about 1760, women in Britain and France made a splash in painting, engraving and even, sculpturing. Most famous are today the painters Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun and Angelika Kauffmann, both superstars of their time. However, many more women made careers in the art scene. Let me introduce you to 10 British female artists from all ranks of life.
Continue reading